Clin Cancer Res. 2006 Jan 15;12(2):662-8.
Research misconduct? Image duplication? Fabrication? Falsification? Unintentional and inadvertent mistake? Coincidental similarity? Cytokine Research Laboratory, Department of Experimental Therapeutics, The University of Texas MD Anderson Cancer Center, Houston, TX, USA.
2012/01/21
Resveratrol inhibits proliferation, induces apoptosis, and overcomes chemoresistance through down-regulation of STAT3 and nuclear factor-kappaB-regulated antiapoptotic and cell survival gene products in human multiple myeloma cells.
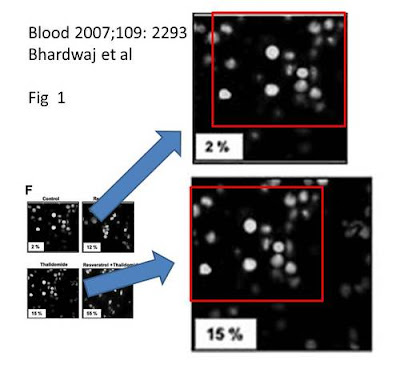
Blood. 2007 Mar 15;109(6):2293-302. Epub 2006 Dec 12.
Resveratrol inhibits proliferation, induces apoptosis, and overcomes chemoresistance through down-regulation of STAT3 and nuclear factor-kappaB-regulated antiapoptotic and cell survival gene products in human multiple myeloma cells.
Flavopiridol suppresses tumor necrosis factor-induced activation of activator protein-1, c-Jun N-terminal kinase, p38 mitogen-activated protein kinase (MAPK), p44/p42 MAPK, and Akt, inhibits expression of antiapoptotic gene products, and enhances apoptosis through cytochrome c release and caspase activation in human myeloid cells.
Mol Pharmacol. 2008 May;73(5):1549-57. Epub 2008 Feb 20.
Flavopiridol suppresses tumor necrosis factor-induced activation of activator protein-1, c-Jun N-terminal kinase, p38 mitogen-activated protein kinase (MAPK), p44/p42 MAPK, and Akt, inhibits expression of antiapoptotic gene products, and enhances apoptosis through cytochrome c release and caspase activation in human myeloid cells.
Modification of cysteine residue in p65 subunit of nuclear factor-kappaB (NF-kappaB) by picroliv suppresses NF-kappaB-regulated gene products and potentiates apoptosis.
Cancer Res. 2008 Nov 1;68(21):8861-70.
Modification of cysteine residue in p65 subunit of nuclear factor-kappaB (NF-kappaB) by picroliv suppresses NF-kappaB-regulated gene products and potentiates apoptosis.
Source
Department of Experimental Therapeutics, Cytokine Research Laboratory, The University of Texas MD Anderson Cancer Center, Houston, Texas 77030, USA.
Blood. 2009 Feb 26;113(9):2003-13. Epub 2008 Oct 24.
Modification of the cysteine residues in IkappaBalpha kinase and NF-kappaB (p65) by xanthohumolleads to suppression of NF-kappaB-regulated gene products and potentiation of apoptosis inleukemia cells.
Source
Cytokine Research Laboratory, Department of Experimental Therapeutics, University of Texas M. D. Anderson Cancer Center, Houston, TX 77030, USA
Figure 4D - p65C38S +/- Picroliv. Right 2 lanes are cloned.
Zerumbone abolishes RANKL-induced NF-kappaB activation,inhibits osteoclastogenesis, and suppresses human breastcancer-induced bone loss in athymic nude mice.
Cancer Res. 2009 Feb 15;69(4):1477-84. Epub 2009 Feb 3.
Zerumbone abolishes RANKL-induced NF-kappaB activation,inhibits osteoclastogenesis, and suppresses human breastcancer-induced bone loss in athymic nude mice.
Thymoquinone poly (lactide-co-glycolide) nanoparticles exhibitenhanced anti-proliferative, anti-inflammatory, andchemosensitization potential.
Biochem Pharmacol. 2010 Jun 1;79(11):1640-7. Epub 2010 Jan 25.
Thymoquinone poly (lactide-co-glycolide) nanoparticles exhibitenhanced anti-proliferative, anti-inflammatory, andchemosensitization potential.
登録:
コメント (Atom)